Data security is one of the most important topics in today’s businesses. One of the most forgotten steps in IT asset management is the retirement of hard drives and other magnetic media. The most effective way to eliminate data on a hard drive is degaussing, you may ask, “What is Degaussing a Hard Drive?” Keep reading.
- Hard drives use magnetic fields to store data on discs called platters.
- Degaussing a hard drive is eliminating the magnetic field patterns.
- A degausser of the appropriate strength will eliminate all of the magnetic fields thereby eliminating all data.
.jpg?width=1000&height=342&name=before-after-degauss%20(2).jpg)
Why Degauss?
- Degaussers destroy all data in approximately 1/10th of a second regardless of whether the drive is functioning or non-functioning
- After degaussing, the data is not recoverable and no longer exists, leaving your media safe for recycling or disposal
- Degaussing a hard drive is recognized by the NSA and DoD as a secure data destruction method
How Does a Degausser Work?
Degaussers, like the Garner TS-1XT NSA listed degausser, erase data by generating a powerful magnetic field that permanently remove the magnetic properties on the disk platters or tape thereby erasing or randomizing the recorded data patterns.
Overwriting/Secure Erase
Overwriting is a method where a random pattern of usually “1” and “0” is written to every part of the drive, frequently three times, to obliterate the underlying data. The advantage of this method is the drive can be re-used. However, there are several disadvantages with Overwriting:
- Only adds layers to existing data, the underlying data still remains and is susceptible to forensic recovery
- Requires a skilled operator to ensure the overwriting is done correctly
- Non-functioning sectors of the hard drive cannot be overwritten allowing data to remain on the drive
- Because Overwriting is not regarded as fail-safe, it is not permitted for the highest data security standards such as the NSA or DoD
- Nearly five times the cost of degaussing because it requires a considerable amount of time (hours) and electricity
Physical Destruction
Drilling holes, hitting with a hammer, running over with a truck etc. will not get rid of data. It will only make the data more difficult to recover. Check out www.drivesavers.com website and see the data they have recovered. Very enlightening.

Physical destruction of hard drives by shredding, bending, and breaking the hard drive and its internal components, prevents the hard drive from “spinning up” or the hard disk platters from being removed and placed on a spin stand used in laboratory data recovery techniques. It is important to recognize, physical destruction damages the media but the data is still present. An 1″ hard drive fragment can contain up to 125 GB of data or 312 pallets of typed paper. Best practices dictate the hard drive first be degaussed before it is physically destroyed.


After erasing a hard drive with a degausser of appropriate magnetic field strength, there is 0% chance of hard drive data recovery as the data is gone!
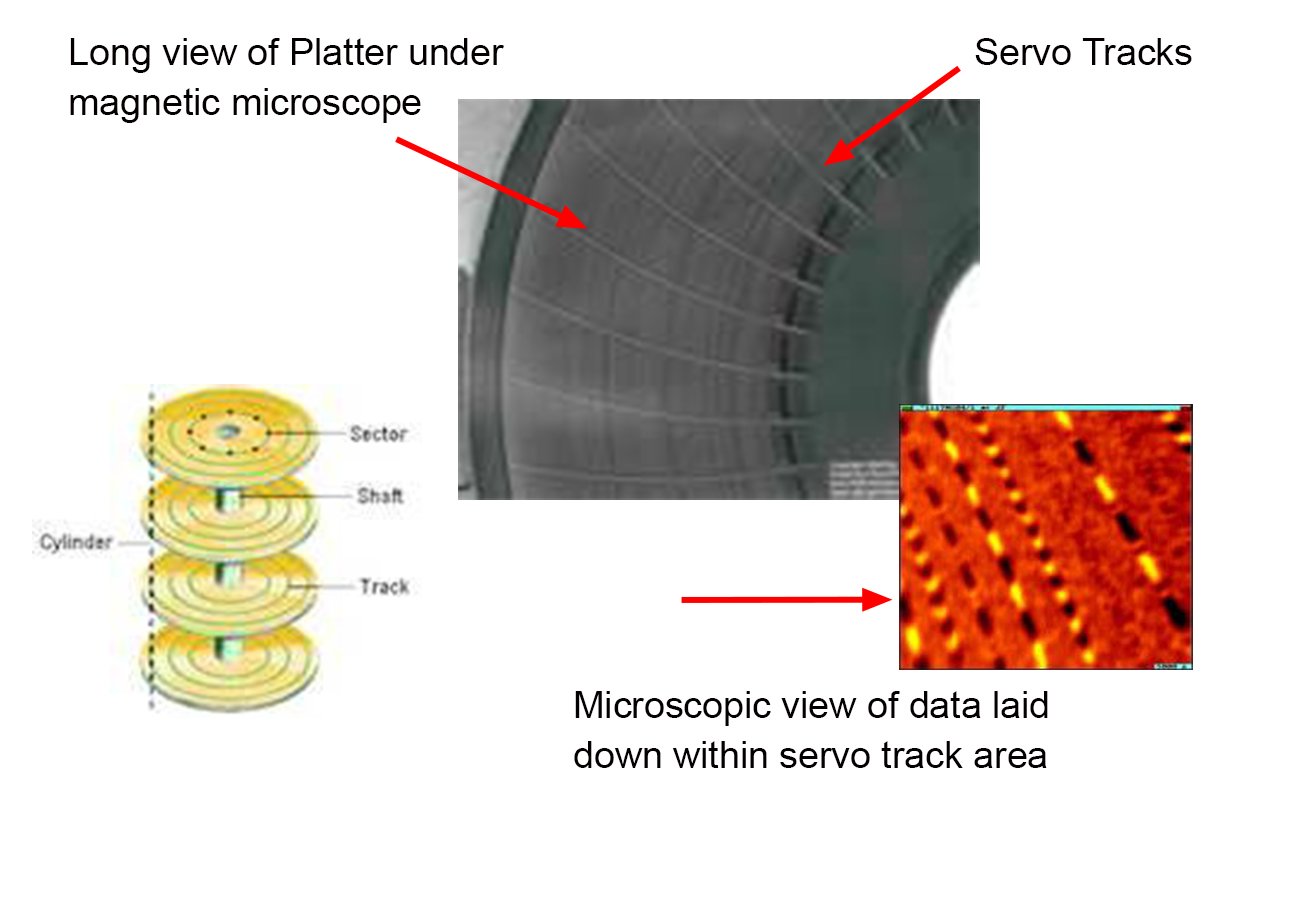
Anatomy of a Hard Disk Drive
Inside a Hard Drive

TS-1XT IRONCLAD
NSA-listed degausser with IRONCLAD Erasure and Destruction Verification System generates a proof-of-destruction certificate with JPG images.
Learn More

HD-3XTL IRONCLAD
High-volume degausser erases all data on hard drives and tapes in under 6 seconds. IRONCLAD automatically generates a certificate and report to prove it.
Learn More

HD-2XT IRONCLAD
Economical and fast degausser erases all data on hard drives and tapes in under 7 seconds. IRONCLAD automatically generates a certificate and report to prove it!
Learn More

PD-5 IRONCLAD
NSA-listed PD-5 hard drive and solid-state physical destroyer with IRONCLAD provides verification by imaging, tracking, and documenting the destroyed media.
Learn More







LEAVE A REPLY